In recent years, we Mongolians have been making great efforts to find new energy sources, introducing technology for extracting synthetic natural gas from coal and intensively exploring and researching methane gas in coal seams. As a result, the project of a synthetic natural gas extraction plant from coal has been fully developed, and methane gas deposits in several coal seams have been discovered.
The fact that we come across terms like methane gas, greenhouse gas, and natural gas at every step may be a sign of the above. However, despite success and achievements, due to the lack of information, the public has a widespread misconception about greenhouse gases, natural gas, and methane gas. Therefore, explaining the terms of these different gases is necessary to eliminate the information gap.
Greenhouse gases are naturally occurring gases such as water vapor (H2O), carbon dioxide (CO2), methane gas (CH4), nitrogen dioxide (N2O), ozone (O3), and other gases that accumulate in the Earth’s atmosphere and affect climate change. These substances make up about 1% of the Earth’s atmosphere but contribute to the greenhouse effect, accelerating climate change. 36–72% of the greenhouse effect is conditioned by water vapor and clouds, 9–26% by carbon dioxide, 4–6% by methane gas, and 3–7% by ozone.
Natural gas is a combustible mineral composed of methane (60-90 %) gas). The composition of natural gas includes hydrocarbons such as ethane, propane, butane, and pentane and a small amount of carbon dioxide, nitrogen, helium, and hydrogen sulfide. Let’s expand on Methane gas, which is common to these two types of gas. Methane gas is released from mining, production, and transportation of coal, natural gas, oil, urban waste, agriculture, farming, burning of organic materials, and decomposition of organic matter in wastewater treatment plants.
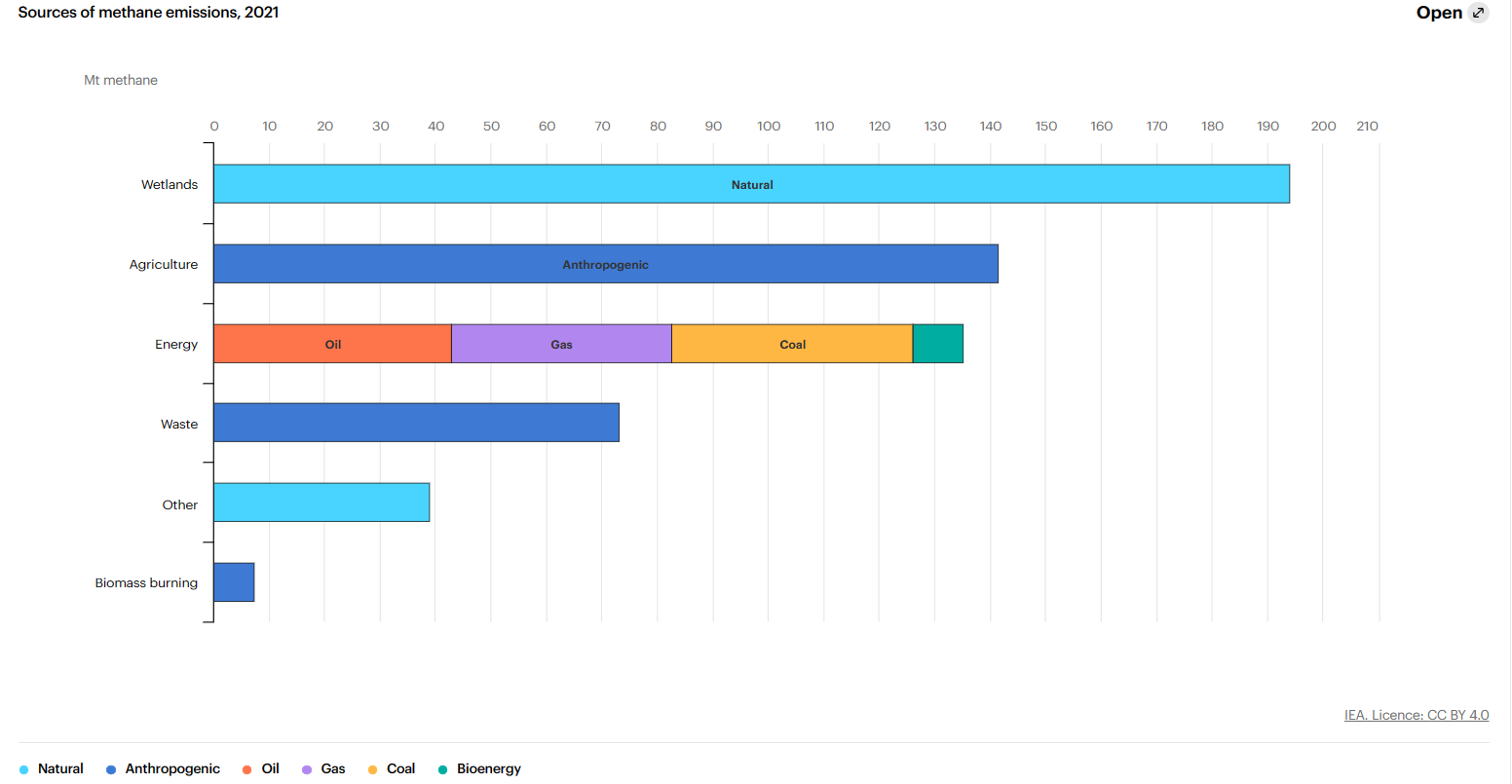
Methane gas is an alkane chemical compound with molecular formula CH4, specific gravity of 16.04 grams/mol, heat release capacity of 55.5 MJ/kg, and ability to remain in the atmosphere for 12 years without decomposition. Although methane gas accounts for 16% of greenhouse gases, it can produce 80 times more greenhouse effect than carbon dioxide over 20 years. Although it is a powerful greenhouse gas, it is a gas that has a high ability to release heat and is a source of energy. There are a wide variety of views on methane, and here are a few. For example, there is a section saying that methane gas is a gas that affects climate change and should not be used. However, releasing methane gas into the atmosphere increases the greenhouse effect and accelerates climate change.
However, it is essential to prevent the open release of methane gas into the atmosphere in all possible forms or to reduce emissions by using them before they are released into the atmosphere, to prevent climate change shortly, to limit the increase in global temperature to 1.5˚C, and to meet the goals of the Paris Agreement. On the other hand, there is an opinion that when methane gas is used for energy, carbon dioxide is released into the atmosphere and affects climate change. True, carbon dioxide is released when methane gas is burned. However, carbon dioxide has 80 times less greenhouse effect than methane gas over 20 years and 28 times less ability to retain heat.
According to the researchers, burning methane gas emitted from abandoned and used coal mines, natural gas and oil extraction, urban landfills, and the decomposition of organic matter in wastewater treatment plants for energy purposes can reduce the greenhouse effect by 96.4%.
Implementing coalbed methane gas or synthetic natural gas extraction projects will help us achieve our commitments to global initiatives to fight climate change, eliminate energy dependence, get new energy sources, reduce air pollution in urban areas, and export products. It is crucial to increase the GDP by adding a variety of products.
B. Bayarjargal, a CEO of Greentrends – Environmental Services.
Source: Mineral Resources Review


